VIGAS DOBLEMENTE APOYADAS
RESUMEN DE CASOS
Pulsa en el diagrama para ir al caso elegido:
CASO 1

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga puntual no centrada.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA
para:

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 2
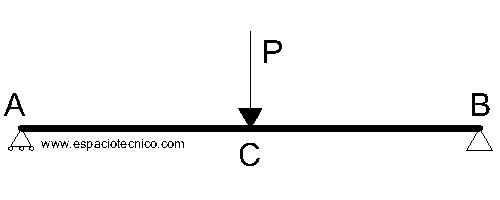
Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga puntual centrada.
REACCIONES
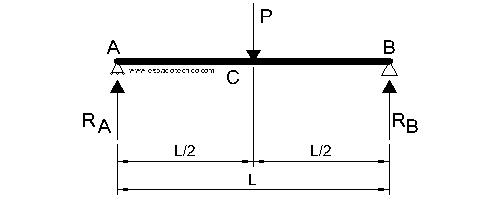
E. CORTANTES
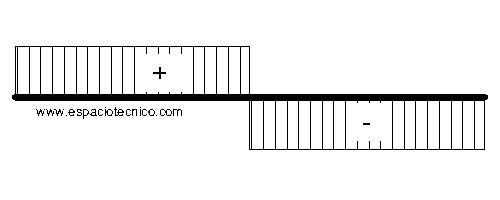
M. FLECTORES
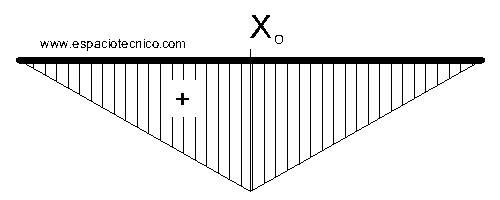
EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 3

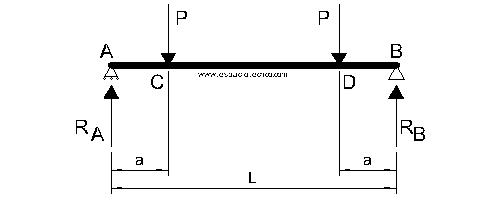
Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con dos carga puntuales iguales y simétricas.
REACCIONES
E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA
para:

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 4

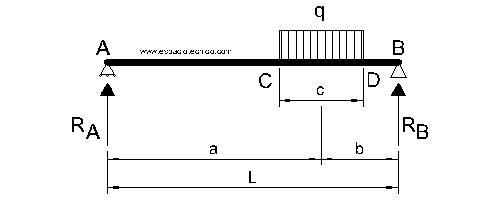
Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida aislada que no empieza ni termina en los apoyos.
REACCIONES
E. CORTANTES
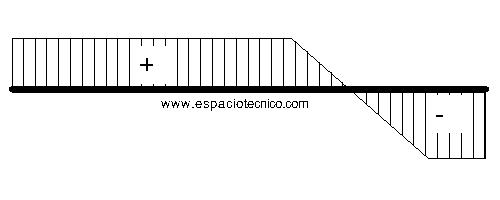
M. FLECTORES
para:

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 5

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida aislada que comienza en un apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES
para:

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA
para:

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 6

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga uniformemente repartida entre apoyos.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 7
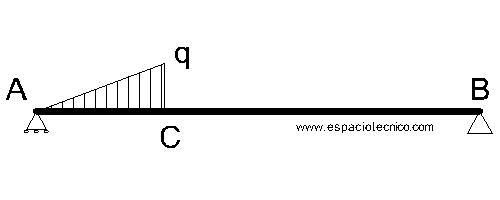
Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga no uniformemente repartida aislada que comienza en un apoyo según esquema.
REACCIONES
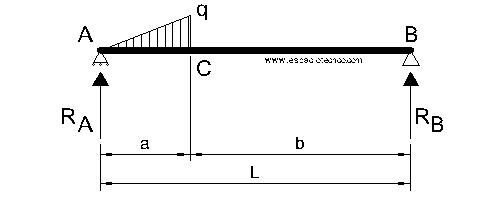
E. CORTANTES
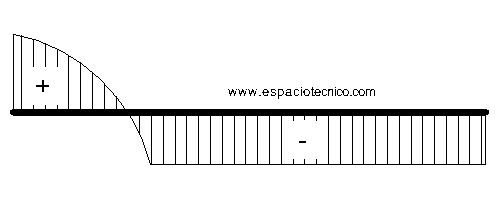
M. FLECTORES
para:
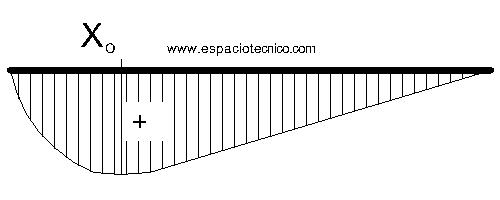
EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA
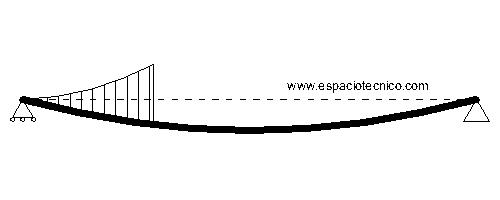
ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 8

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga no uniformemente repartida aislada que comienza en un apoyo según esquema.
REACCIONES
E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES
para:

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
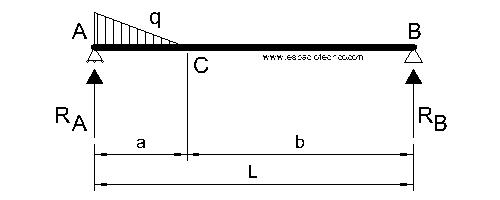
CASO 9

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga no uniformemente repartida de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES
E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 10

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con dos cargas simetricas no uniformemente repartidas de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
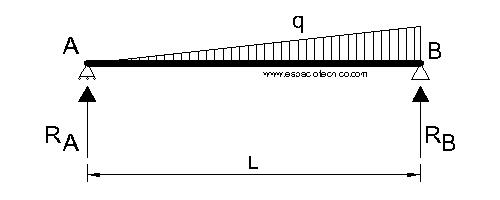
CASO 11

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida triangular no simétrica de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
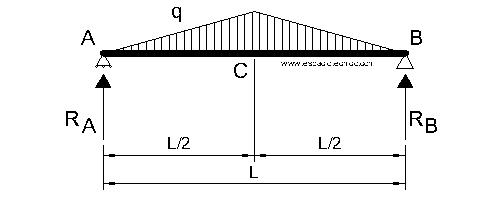
CASO 12

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida triangular simétrica de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES
E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 13

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida trapezoidal de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES
para:

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 14

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con una carga repartida trapezoidal simetrica de apoyo a apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 15

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con un momento en un apoyo.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 16

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con dos momentos, uno en cada apoyo según esquema.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 17

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con dos momentos, uno en cada apoyo según esquema.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA

ÁNGULOS DE GIRO
CASO 18

Definición
Viga apoyada-apoyada con un momento aislado.
REACCIONES

E. CORTANTES

M. FLECTORES

EC. ELÁSTICA
FLECHA
